Abstract
Green finance plays an important role in helping countries achieve sustainable development goals. It brings many benefits to both individuals and businesses, such as: encouraging the dissemination of technology and developing environmentally friendly infrastructure, creating comparative advantages and improving economic prospects. This study aims to present the concepts and benefits of green finance, analyze the current status of implementing some types of green finance in Vietnam, and propose some solutions for developing green finance in Vietnam in the coming time.
CONCEPT AND TYPES OF GREEN FINANCE
Concept of green finance
According to Sachs et al. (2019), green finance refers to a broad portfolio of activities, products, services (including: financial risk, climate and environmental management), instruments and mechanisms in the financial sector linked to investments in business and industrial activities that can create sustainable operations, positive impacts on society and the environment, including land, water, biodiversity, air and people.
Green finance can be understood in the simplest way as a set of strategies and methods to achieve or mobilize and allocate funds (both private and public, as well as philanthropic contributions) to close the large investment gap in creating and maintaining new, climate-resilient, sustainable infrastructure. This will help countries address many societal challenges, meet their climate action commitments and national determination to contribute in line with the Paris Agreement and achieve the seventeen United Nations Sustainable Development Goals in the current decade from 2021 to 2030 (Nawaz et al., 2021).
Types of green finance
There are several terms that are widely used to express the concept, form and form of green finance as follows:
– Carbon finance: Financial instruments based on the economic value of carbon emissions that an organization cannot avoid, but it compensates by funding other organizations for offset projects that contribute to reducing carbon emissions (Sachs et al., 2019). Carbon trading or carbon cap and trade is a form of carbon trading, targeting carbon emissions (in tonnes or CO2 equivalent units).
– Green bonds: Proceeds are only used to finance or refinance projects with clear environmental benefits (Dou and Qi, 2019).
– Green stocks are understood as stocks of enterprises operating in the field of efficient use of energy, clean fuels, renewable energy, natural resources, water resources, environmental pollution reduction and supporting materials towards the goal of sustainable economic development. In essence, bonds and stocks belong to securities, so the green stock market has a similar structure to the green bond market. Market participants include issuers, investors, regulatory mechanisms and credit rating organizations. Green capital mobilization tools and green stock indices can develop if green financial markets develop; On the contrary, the more diverse and abundant green securities are, the more they support market development and increase liquidity for the green financial market (Tran Thi Thanh Tu and Do Hong Nhung, 2018).
– Green funds: Debt and equity financing provide customers with a platform for long-term financing of environmentally friendly businesses and organizations (Jin and Han, 2018).
– Green credit: Project loans (mainly mortgages) and industrial loans can be facilitated through green deposits (Wang et al., 2021).
– Climate finance: Finance that promotes the climate resilience of infrastructure, as well as social and economic assets (Fang et al., 2021).
STATUS OF GREEN FINANCE DEVELOPMENT
Policies and guidelines for green finance development
In order to promote green finance in Vietnam, the State has issued many policy documents to guide green finance development, typically: Law on Environmental Protection (2020), Decision No. 1393/QD-TTg, dated September 25, 2012 of the Prime Minister approving the National Strategy on Green Growth; Decision No. 403/QD-TTg, dated March 20, 2014 of the Prime Minister approving the National Action Plan on Green Growth for the period 2014-2020; Decision No. 1658/QD-TTg, dated October 1, 2021 approving the National Strategy on Green Growth for the period 2021-2030, with a vision to 2050; Decree No. 06/2022/ND-CP, dated January 7, 2022 on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and protecting the ozone layer; Decision No. 882/QD-TTg, dated July 22, 2022 approving the National Action Plan on Green Growth for the 2021-2030 period.
In order to implement the National Strategy on Green Growth for the 2021-2030 period, on August 15, 2024, the Ministry of Finance issued Decision No. 1934/QD-BTC approving the Action Plan of the Ministry of Finance to implement the National Strategy on Green Growth for the 2021-2030 period. In addition, mobilizing resources from
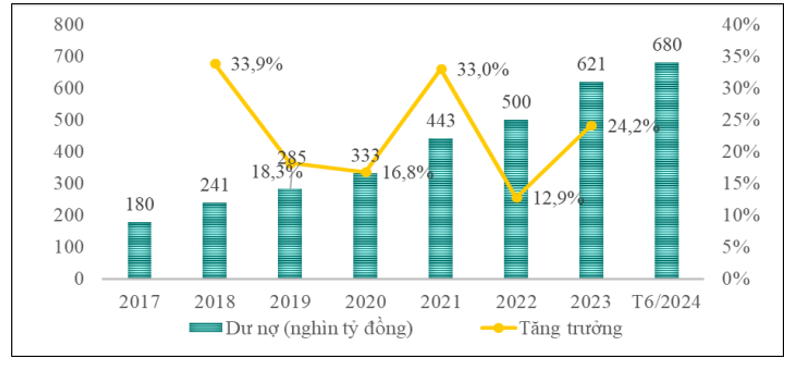 |
| Nguồn: Ngân hàng Nhà nước |
Abstract
Green finance plays an important role in helping countries achieve sustainable development goals. It brings many benefits to both individuals and businesses, such as: encouraging the dissemination of technology and developing environmentally friendly infrastructure, creating comparative advantages and improving economic prospects. This study aims to present the concepts and benefits of green finance, analyze the current status of implementing some types of green finance in Vietnam, and propose some solutions for developing green finance in Vietnam in the coming time.
CONCEPT AND TYPES OF GREEN FINANCE
Concept of green finance
According to Sachs et al. (2019), green finance refers to a broad portfolio of activities, products, services (including: financial risk, climate and environmental management), instruments and mechanisms in the financial sector linked to investments in business and industrial activities that can create sustainable operations, positive impacts on society and the environment, including land, water, biodiversity, air and people.
Green finance can be understood in the simplest way as a set of strategies and methods to achieve or mobilize and allocate funds (both private and public, as well as philanthropic contributions) to close the large investment gap in creating and maintaining new, climate-resilient, sustainable infrastructure. This will help countries address many societal challenges, meet their climate action commitments and national determination to contribute in line with the Paris Agreement and achieve the seventeen United Nations Sustainable Development Goals in the current decade from 2021 to 2030 (Nawaz et al., 2021).
Types of green finance
There are several terms that are widely used to express the concept, form and form of green finance as follows:
– Carbon finance: Financial instruments based on the economic value of carbon emissions that an organization cannot avoid, but it compensates by funding other organizations for offset projects that contribute to reducing carbon emissions (Sachs et al., 2019). Carbon trading or carbon cap and trade is a form of carbon trading, targeting carbon emissions (in tonnes or CO2 equivalent units).
– Green bonds: Proceeds are only used to finance or refinance projects with clear environmental benefits (Dou and Qi, 2019).
– Green stocks are understood as stocks of enterprises operating in the field of efficient use of energy, clean fuels, renewable energy, natural resources, water resources, environmental pollution reduction and supporting materials towards the goal of sustainable economic development. In essence, bonds and stocks belong to securities, so the green stock market has a similar structure to the green bond market. Market participants include issuers, investors, regulatory mechanisms and credit rating organizations. Green capital mobilization tools and green stock indices can develop if green financial markets develop; On the contrary, the more diverse and abundant green securities are, the more they support market development and increase liquidity for the green financial market (Tran Thi Thanh Tu and Do Hong Nhung, 2018).
– Green funds: Debt and equity financing provide customers with a platform for long-term financing of environmentally friendly businesses and organizations (Jin and Han, 2018).
– Green credit: Project loans (mainly mortgages) and industrial loans can be facilitated through green deposits (Wang et al., 2021).
– Climate finance: Finance that promotes the climate resilience of infrastructure, as well as social and economic assets (Fang et al., 2021).
STATUS OF GREEN FINANCE DEVELOPMENT
Policies and guidelines for green finance development
In order to promote green finance in Vietnam, the State has issued many policy documents to guide green finance development, typically: Law on Environmental Protection (2020), Decision No. 1393/QD-TTg, dated September 25, 2012 of the Prime Minister approving the National Strategy on Green Growth; Decision No. 403/QD-TTg, dated March 20, 2014 of the Prime Minister approving the National Action Plan on Green Growth for the period 2014-2020; Decision No. 1658/QD-TTg, dated October 1, 2021 approving the National Strategy on Green Growth for the period 2021-2030, with a vision to 2050; Decree No. 06/2022/ND-CP, dated January 7, 2022 on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and protecting the ozone layer; Decision No. 882/QD-TTg, dated July 22, 2022 approving the National Action Plan on Green Growth for the 2021-2030 period.
In order to implement the National Strategy on Green Growth for the 2021-2030 period, on August 15, 2024, the Ministry of Finance issued Decision No. 1934/QD-BTC approving the Action Plan of the Ministry of Finance to implement the National Strategy on Green Growth for the 2021-2030 period. In addition, mobilizing resources from



